

How Healthcare Organizations Can Streamline HIPAA Vendor Compliance
Learn how to efficiently manage HIPAA compliance for vendor relationships in healthcare.
The Critical Role of HIPAA Compliance in Healthcare Vendor Management
Healthcare organizations operate within a highly regulated landscape, with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) standing as a cornerstone of patient privacy and data security. However, the complexity of healthcare operations extends far beyond internal systems; it encompasses a vast network of third-party vendors, each of whom may have access to, transmit, or store Protected Health Information (PHI). Managing HIPAA compliance for these vendor relationships presents unique and significant challenges. With the increasing digitization of healthcare data, the proliferation of cloud-based services, and the growing complexity of vendor relationships, ensuring that every touchpoint adheres to stringent HIPAA regulations has become more critical than ever. The stakes are incredibly high, as non-compliance can lead to severe financial penalties, reputational damage, and, most importantly, a profound breach of patient trust.
The financial burden of HIPAA compliance for healthcare organizations is substantial. Recent studies and industry reports consistently indicate that healthcare organizations spend a significant amount on maintaining HIPAA compliance, with figures often averaging around $8.3 million annually. A considerable portion of these costs is directly attributable to vendor management, including due diligence, ongoing monitoring, contract management, and audit preparation. This expense highlights the sheer administrative overhead and the extensive resources required to manage vendor relationships effectively while upholding HIPAA standards. The challenge is not just about avoiding fines; it's about safeguarding sensitive patient data against an ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats and ensuring that every entity within the healthcare ecosystem is a reliable guardian of privacy.
The proliferation of specialized healthcare technology, billing services, data analytics providers, and even marketing firms means that almost every external partner a healthcare organization engages with could be classified as a Business Associate under HIPAA. This designation triggers a cascade of compliance obligations, demanding that these vendors adhere to the same rigorous privacy and security standards as the healthcare organization itself. The inherent difficulty lies in the sheer volume of vendors, the diverse nature of their services, and the varying degrees of access they require to PHI. Without a streamlined, robust, and proactive approach to vendor compliance, healthcare organizations risk unknowingly exposing themselves to vulnerabilities, making robust and efficient vendor compliance a non-negotiable aspect of modern healthcare management. This section lays the groundwork for understanding why effective vendor compliance is so vital in this sensitive industry.
Understanding HIPAA Vendor Requirements
For healthcare organizations, navigating the intricate landscape of HIPAA compliance extends directly to their vendor relationships. Under HIPAA, most third-party vendors who create, receive, maintain, or transmit Protected Health Information (PHI) on behalf of a Covered Entity (like a hospital or clinic) are classified as Business Associates (BAs). This classification triggers specific legal obligations for both the Covered Entity and the Business Associate, designed to ensure the proper handling of PHI and strict adherence to all privacy and security regulations. Understanding these core requirements is the foundation for effective vendor compliance.
Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
A Business Associate Agreement (BAA) is not merely a formality; it is a legally required contract between a Covered Entity and its Business Associate. These agreements are paramount because they clearly define the permissible uses and disclosures of PHI by the vendor, establish the required security measures they must implement, and outline their responsibilities in protecting patient data. A comprehensive BAA should meticulously detail the scope of PHI access, specify security safeguards such as encryption and access controls, articulate breach notification protocols, and stipulate the vendor's agreement to comply with all relevant HIPAA rules. Without a robust BAA in place, any PHI breach originating from a vendor becomes the direct responsibility of the healthcare organization, leading to severe consequences. Ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and enforceability of every BAA is a foundational aspect of HIPAA vendor compliance.
PHI Handling Procedures and Safeguards
Beyond the BAA, healthcare organizations must ensure that their vendors implement detailed, verifiable protocols for the secure handling, storage, and transmission of Protected Health Information. This encompasses a range of technical, physical, and administrative safeguards. Technical safeguards include encryption for data at rest and in transit, robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure coding practices. Physical safeguards involve limiting physical access to facilities and equipment where PHI is stored or processed, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas. Administrative safeguards involve policies and procedures for workforce training, risk management, and internal audits. Any vendor handling PHI must demonstrate that their internal processes and systems are designed and regularly reviewed to prevent unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of sensitive patient data. This requires ongoing vigilance and validation, not just a one-time check.
The implications of these requirements are far-reaching. Healthcare organizations are not only responsible for their own compliance but are also accountable for ensuring their Business Associates uphold HIPAA standards. This necessitates robust due diligence before engaging a vendor, comprehensive contracting (the BAA), and continuous monitoring throughout the vendor relationship. A failure at any point in this chain can result in significant legal and financial repercussions, underscoring the vital importance of a thorough understanding and consistent application of these core HIPAA vendor requirements.
Key Compliance Areas
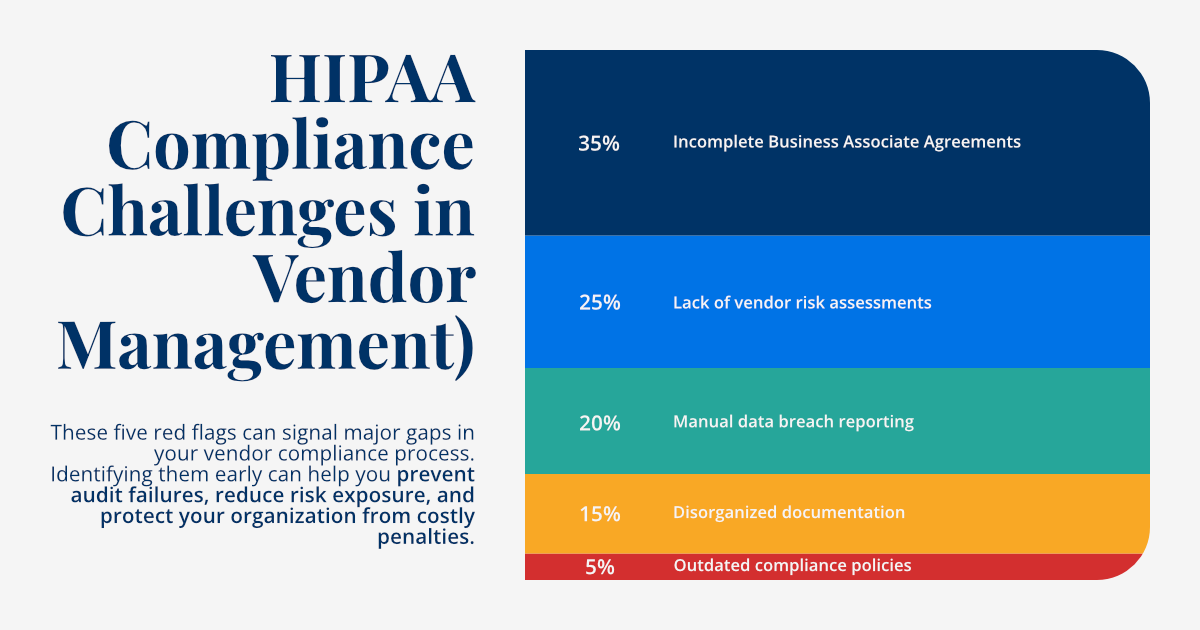
Delving deeper into HIPAA vendor compliance, several critical areas demand meticulous attention beyond the foundational Business Associate Agreements and general PHI handling procedures. These specific domains are often where vulnerabilities reside and where enforcement actions frequently originate. Comprehensive management of these areas is essential for truly safeguarding patient data and ensuring your vendors remain compliant with the letter and spirit of HIPAA.
- Security Measures: This encompasses the meticulous implementation of appropriate technical, physical, and administrative safeguards to protect PHI. Technical safeguards include encryption for data at rest and in transit, robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure coding practices. Physical safeguards involve limiting physical access to facilities and equipment where PHI is stored or processed, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive areas. Administrative safeguards refer to the policies and procedures that govern employee conduct, risk analysis, and regular security training. Healthcare organizations must verify that their vendors have robust security frameworks in place that align with or exceed HIPAA's requirements. This often involves security audits, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments conducted either by the vendor or by the healthcare organization itself.
- Incident Response: A well-defined and rigorously tested incident response plan is not merely a recommendation; it's a critical requirement under HIPAA. Healthcare organizations must ensure their vendors have comprehensive protocols for identifying, containing, reporting, and responding to potential PHI breaches or security incidents. This includes clear lines of communication, established timelines for reporting, and procedures for forensic analysis and remediation. The BAA should explicitly outline the vendor's responsibilities in the event of an incident, including notification requirements to the Covered Entity, assisting in investigations, and providing necessary documentation for regulatory reporting. A slow or inadequate response from a vendor can escalate a minor incident into a major, reportable breach, with significant consequences for the Covered Entity.
- Access Controls: Strict management of PHI access rights and regular review of access privileges are fundamental to HIPAA compliance. Vendors must implement robust access control mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to PHI, and only to the extent necessary to perform their specified duties. This principle of "minimum necessary access" is central to HIPAA. This includes detailed logging of all access attempts, both successful and unsuccessful, and periodic audits of access logs to detect unusual patterns or unauthorized activity. Additionally, processes for promptly revoking access for terminated employees or when a vendor's contract ends are crucial. The lack of granular access controls or inadequate oversight of who can access PHI is a common source of compliance violations and data breaches.
By focusing on these key compliance areas with a detailed and proactive approach, healthcare organizations can significantly strengthen their HIPAA vendor compliance program. This targeted focus not only helps in meeting regulatory obligations but also builds a stronger defense against the ever-present threat of data breaches and cyberattacks that could compromise patient trust and organizational integrity.
Automation Benefits
The immense challenges of managing HIPAA compliance across a large and dynamic vendor ecosystem often overwhelm traditional, manual processes. The sheer volume of documentation, the need for continuous monitoring, and the complexity of regulatory requirements make manual oversight prone to errors, inefficiencies, and significant compliance gaps. This is precisely where modern automation, particularly AI-powered solutions, offers a transformative pathway for healthcare organizations to streamline HIPAA vendor compliance, ensuring greater accuracy, efficiency, and ultimately, stronger data security.
Automated BAA Management
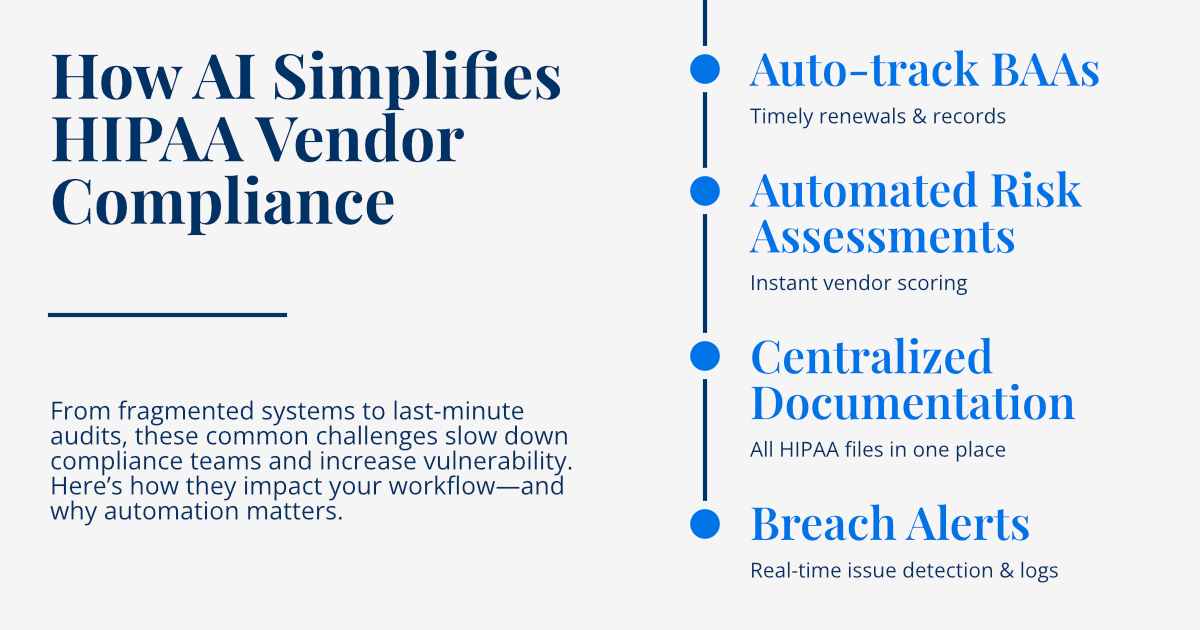
Automating the lifecycle of Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) offers profound benefits. AI-powered platforms can streamline the creation, negotiation, tracking, and renewal of BAAs. This includes intelligent contract analysis using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to ensure that all necessary HIPAA clauses are included and that the terms align with organizational policies. Automated systems can trigger alerts for upcoming BAA expirations, initiate renewal processes, and even highlight deviations from standard terms. This drastically reduces manual administrative burden, minimizes the risk of outdated or incomplete agreements, and ensures that every vendor relationship is legally secure and compliant from the outset, leading to automated compliance checks that verify adherence to predefined legal and security standards.
Continuous Monitoring and Risk Assessment
Perhaps one of the most transformative benefits of automation is the ability to implement continuous monitoring of vendor activities and their compliance status. Unlike traditional periodic reviews, automated systems provide real-time or near real-time insights into potential compliance violations or emerging risks. This includes monitoring for changes in a vendor's security posture, identifying anomalies in data access patterns, or tracking industry news for any reported breaches or regulatory actions against a vendor. Automated alerts for potential non-compliance enable healthcare organizations to react swiftly, initiating investigations and remediation efforts before a minor issue escalates into a major breach. This proactive approach significantly reduces the "blind spots" inherent in manual, time-bound monitoring efforts, providing a far more robust and dynamic risk management framework.
Beyond these core benefits, automation also contributes to improved audit readiness, enhanced data accuracy, and a more efficient allocation of compliance resources. By automating routine and data-intensive tasks, compliance teams can shift their focus from administrative burdens to strategic analysis, risk mitigation, and continuous improvement of the compliance program. This not only strengthens HIPAA compliance but also contributes to the overall security and operational efficiency of the healthcare organization.
Implementation Best Practices
While the benefits of automating HIPAA vendor compliance are clear, successful implementation requires more than just adopting new technology. It demands a strategic approach, careful planning, and a commitment to integrating these solutions seamlessly into existing workflows. Adhering to best practices ensures that the transition to an automated system is smooth, effective, and delivers the intended improvements in compliance and security posture.
- Comprehensive Vendor Onboarding: The compliance journey with any vendor begins long before a contract is signed. Implement a thorough and standardized vendor onboarding process that includes a meticulous assessment of the vendor's capabilities, their existing security safeguards, and their overall compliance readiness against HIPAA requirements. This initial due diligence should involve detailed questionnaires, security assessments, and, where appropriate, onsite audits to verify their stated capabilities. Automated platforms can streamline this initial vetting, providing consistent evaluation criteria and flagging any immediate red flags, ensuring that only compliant vendors are brought into your ecosystem.
- Regular Compliance Audits: While continuous monitoring provides real-time insights, scheduled, in-depth compliance audits of vendor status and security measures remain a crucial best practice. These audits can be triggered automatically by your compliance system based on a risk-based schedule (e.g., higher-risk vendors audited more frequently). Audits should cover a wide range of areas, including adherence to BAA terms, verification of security controls, review of access logs, and validation of incident response plans. Automated tools can facilitate the audit process by simplifying data collection, providing standardized checklists, and generating comprehensive reports, making audits more efficient and less disruptive.
- Automated Documentation and Reporting: A key benefit of automation is the ability to maintain meticulous and digital tracking of all compliance-related activities, decisions, and communications. Every interaction with a vendor, every assessment completed, every policy update, and every remediation effort should be automatically logged and stored in a centralized, secure repository. This automated documentation creates an irrefutable audit trail, which is indispensable during regulatory reviews, internal audits, or in the event of a breach investigation. It significantly reduces the administrative burden of manual record-keeping and ensures that your organization is always audit-ready with complete, accurate, and easily retrievable evidence of due diligence.
- Continuous Monitoring and Adaptive Risk Management: Beyond initial assessments, continuous oversight of vendor activities and their compliance status is paramount. This involves leveraging automated systems to continuously monitor external threat intelligence feeds, public records for data breaches, and a vendor's security ratings. Furthermore, setting up real-time alerts for any deviations from agreed-upon security postures or compliance requirements ensures that your organization can react swiftly to emerging risks. This continuous, proactive monitoring shifts your compliance strategy from reactive to adaptive, allowing for immediate intervention and minimizing potential damage from vendor-related vulnerabilities.
By diligently applying these implementation best practices, healthcare organizations can build a robust, efficient, and truly secure HIPAA vendor compliance program. This not only helps in meeting stringent regulatory demands but also fortifies the overall security posture of the organization, protecting patient data and preserving trust.
Conclusion: Embracing Automation for HIPAA Compliance
In the intricate and high-stakes world of healthcare, ensuring robust HIPAA vendor compliance is not just a regulatory obligation; it is a fundamental pillar of patient trust, data security, and organizational integrity. The escalating complexity of vendor relationships, coupled with the ever-present threat of data breaches and the severe penalties for non-compliance, underscores the urgent need for healthcare organizations to move beyond outdated, manual compliance methodologies.
Automated HIPAA compliance solutions offer a powerful and indispensable pathway forward. By strategically implementing AI-powered tools and sophisticated automated monitoring systems, healthcare organizations can revolutionize their vendor compliance processes. This transformation enables them to streamline the entire lifecycle of vendor management—from meticulous onboarding and robust Business Associate Agreement (BAA) management to continuous, real-time oversight and seamless audit readiness. The shift to automation significantly reduces the inherent risks associated with human error, enhances the speed and accuracy of compliance activities, and provides an unparalleled level of visibility into the third-party ecosystem.
Ultimately, embracing automation for HIPAA vendor compliance is an investment that yields substantial returns. It allows healthcare organizations to maintain impeccable regulatory adherence, drastically reduce administrative burdens and associated costs, and dramatically improve their overall security posture. By doing so, they not only protect sensitive Protected Health Information (PHI) but also optimize resource allocation, allowing valuable compliance personnel to focus on strategic risk management and policy refinement rather than tedious manual tasks. In a landscape where data security is paramount, automated solutions empower healthcare providers to navigate compliance complexities with confidence, ensuring continuous adherence to HIPAA requirements and fostering enduring patient trust.